Maps Glossary
WhiteClouds builds 3D Raised Relief Maps
Did you know we make
3D raised-relief maps
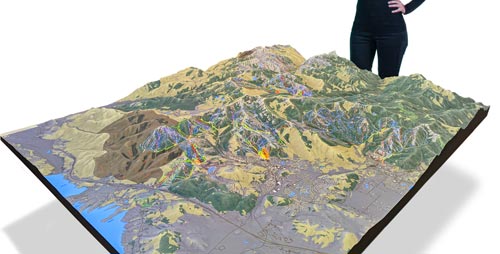
and
3D raised-relief maps

Kame
A kame is a small hill or mound of sediment that is deposited by glacial meltwater. Kames are usually composed of sand and gravel and can vary in size from a few meters to several hundred meters. They are often found in groups and can create distinctive landscapes, such as kame fields. Kames are formed when sediment is carried by meltwater streams and deposited at the edge of a glacier or in the glacier’s meltwater channels. As the glacier retreats, the sediment is left behind, forming a hill or mound.
Karren
Karren are small-scale limestone features that are formed by the dissolution of rock. They are characterized by their irregular shape and are often found on lime stone surfaces. Karren are formed when water flows over the surface of limestone, dissolving the rock and creating small channels and depressions. Over time, these channels can deepen and widen, creating more complex shapes. Karren can take many forms, including rills, runnels, and solution pans.
Karst
Karst is a landscape that is formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks, such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. Karst landscapes are characterized by sinkholes, caves, and underground drainage systems. Karst is created when rainwater or surface water flows over soluble rock, dissolving the rock and creating underground drainage systems. As the water flows through the rock, it can create caves and other underground features. Karst landscapes are found all over the world and can provide important habitats for a variety of plant and animal species.
Kettle
A kettle is a depression or basin that is formed when a block of ice, called a glacier, breaks off and becomes buried in sediment or till. Kettles can vary in size from a few meters to several kilometers and can be found in areas that were covered by glaciers during the last ice age. As the glacier melts, the block of ice becomes buried in sediment, creating a depression in the ground. Kettles can fill with water, forming kettle lakes, or they can remain dry. Kettles can have a significant impact on the landscape, as they can alter the flow of water and affect the distribution of plant and animal species.
Kettle Lake
A kettle lake is a type of lake that is formed by a block of ice, called a kettle, that was left behind by a retreating glacier. Kettle lakes are often circular in shape and can vary in size from small ponds to large lakes. T hey are found in areas that were covered by glaciers during the last ice age and can be found in many different parts of the world. Kettle lakes can be important habitats for a variety of plant and animal species, as well as important recreational areas.
Key
In topography, a key is a list of symbols or colors used on a map to represent features on the map. The key is often located in a corner of the map and is used to help readers interpret the map. The symbols used in a key can represent a variety of features, such as roads, buildings, and bodies of water. The key is an important part of a map, as it allows readers to understand what the various symbols on the map represent.
Key Map
A key map is a small map that is used to show the location of a larger map within a larger area. Key maps are often found on the inside cover of an atlas or in the corner of a larger map. They are used to provide context for the larger map and to help readers understand where the map is located in relation to other areas.
Key Terrain
Key terrain refers to terrain that is important to the success of a military operation. Key terrain can include any feature that provides an advantage or disadvantage to the military, such as hills, valleys, and rivers. Key terrain can affect the movement of troops, the placement of defensive positions, and the ability to conduct offensive operations. The identification and control of key terrain is an important part of military planning and can have a significant impact on the outcome of a battle or campaign.
Kink Band
A kink band is a geological feature that is formed when rock layers bend sharply in a small area. Kink bands are often found in sedimentary rocks and are formed when the layers are subjected to compression or bending forces. The result is a band of rock that appears to be folded or bent at an angle, surrounded by layers of rock that are relatively straight. Kink bands can provide important information about the forces that acted on the rock layers and can be used to reconstruct the geological history of an area.
Knickpoint
A knickpoint is a sharp change in the slope of a river or stream. Knickpoints are often found in areas where the river or stream flows over a layer of harder rock, creating a sudden drop in elevation. The result is a waterfall or rapids, which can create important habitats for aquatic species and provide important recreational opportunities. Knickpoints can also be important indicators of changes in the landscape over time, as they can indicate the presence of geological faults or other features.
Krast
Krast is a geological feature that is formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks, such as limestone or gypsum. Krast features can include sinkholes, caves, and underground drainage systems. Krast is similar to karst, but is a term that is used specifically to describe features that are found in gypsum deposits. Krast features can provide important habitats for a variety of plant and animal species, as well as important recreational opportunities.
Kriging
Kriging is a statistical method that is used in geostatistics to estimate the value of a variable at a specific location. Kriging is often used in environmental studies to estimate the concentration of pollutants in an area, or to estimate the yield of crops in agricultural fields. The method is based on a mathematical model that takes into account the spatial correlation between data points, and can provide more accurate estimates than other statistical methods. Kriging is an important tool for environmental scientists and can help to inform decisions about land use and resource management.