Terrain Maps with Google Maps Look
What is a Terrain Map?
We build 2D and 3D Terrain Maps
Table of Contents
Terrain Maps with Google Maps Look
Terrain maps, also known as topographic maps, are an incredible tool for exploring and understanding the natural world around us. Whether you’re a hiker, a climber, or just someone who loves to explore the great outdoors, terrain maps can help you navigate the landscape and uncover hidden gems you never knew existed. So what exactly are terrain maps with a Google Maps Look? Simply put, they are maps that show the physical features of the earth’s surface and look like Google Maps. They use contour lines to show the elevation and shape of the land, as well as other features such as rivers, lakes, and forests.
One of the most exciting things about terrain maps is that they allow us to visualize the landscape in a way that is not possible through photos or satellite imagery. By looking at a terrain map, you can see the ridges, valleys, and peaks of a mountain range, or the intricate network of canyons and rivers in a desert landscape.
 New Mexico Terrain Map
New Mexico Terrain Map
Terrain maps come in a variety of types and styles. Each type of terrain map provides unique information about the landscape and can be used for different purposes. Let’s explore some of the most common types of terrain maps.
Physical Maps – Physical maps show the natural features of the earth’s surface, such as mountains, rivers, and forests. Physical maps are often color-coded to represent different elevations and can be used to identify geographic features and plan outdoor activities.
Geological Maps – Geological maps show the types of rocks and geological formations in a particular area. Geologists use geological maps to study the composition of the earth’s crust and understand the geological history of a particular region.
Land Use Maps – Land use maps show how the land in a particular area is being used, such as for agriculture, urban development, or conservation. Land use maps can be used to identify areas of environmental concern and plan land use policies.
Aerial Maps – Aerial maps show the landscape from above, often using satellite imagery. Aerial maps can provide a high level of detail and are useful for studying large areas and identifying features such as vegetation cover and land use patterns.
3D Maps – 3D maps provide a three-dimensional representation of the landscape, often using computer modeling or LiDAR technology. 3D maps can be used to study the topography of a particular area and visualize changes in elevation over time.
Bathymetric Maps – Bathymetric maps show the underwater features of the earth’s surface, such as the depth of the ocean floor and the location of underwater features such as coral reefs and shipwrecks. Bathymetric maps are useful for studying the ocean floor and planning oceanographic research.
Nautical Charts – Nautical charts show the topography of the ocean floor and are used for navigation by sailors and mariners. Nautical charts include information about sea depths, underwater hazards, and the location of navigational aids such as buoys and lighthouses.
From outdoor enthusiasts to scientific researchers, terrain maps provide valuable insights into the natural world around us. Listed below are some of the exciting uses of terrain maps.
Navigation – Terrain maps are essential tools for navigation. Hikers, climbers, and backcountry adventurers rely on terrain maps to plan their routes and stay on course. By understanding how to read contour lines, adventurers can determine the elevation, slope, and steepness of an area, allowing them to plan a safe and efficient route. Terrain maps also show the location of features such as rivers, lakes, and campsites, which are crucial for planning a successful trip.
Scientific Research – Terrain maps are a critical tool for scientific research. Geologists, ecologists, and other researchers use terrain maps to study the earth’s surface and gain valuable insights into geological, ecological, and environmental phenomena. Terrain maps can be used to analyze patterns of erosion, vegetation, and geological formations, helping researchers understand the history and evolution of a particular landscape.
Urban Planning – Terrain maps are also useful tools for urban planning. Urban planners can use terrain maps to identify suitable sites for development, assess the environmental impact of proposed projects, and plan transportation infrastructure. By understanding the topography of a particular area, urban planners can design cities that are more efficient, sustainable, and resilient.
Emergency Management – Terrain maps are essential tools for emergency management. In the event of a natural disaster such as a wildfire, earthquake, or flood, emergency responders can use terrain maps to plan evacuation routes, locate safe zones, and assess the impact of the disaster on the landscape. By understanding the topography of a particular area, emergency responders can respond more quickly and effectively to natural disasters.
Education – Terrain maps are excellent tools for education. By studying terrain maps, students can learn about the physical features of the earth’s surface, the forces that shape the landscape, and the ways in which humans interact with the environment. Terrain maps can be used to teach a wide range of subjects, including geography, geology, environmental science, and history.
 Utah Terrain Map
Utah Terrain Map
These maps are filled with a wealth of information about the natural world. From the elevation and slope of the land to the location of rivers and forests, terrain maps provide a detailed and informative representation of the earth’s surface. Some features of terrain maps are:
- Contour Lines – Contour lines are the most recognizable feature of a terrain map. These lines represent the elevation of the land and show the shape of the terrain. By understanding how to read contour lines, you can determine the steepness of a slope, the elevation of a mountain peak, and the depth of a valley.
- Symbols – Terrain maps use symbols to represent natural and man-made features. Symbols can include everything from rivers and lakes to highways and bridges. By understanding these symbols, you can identify important landmarks and plan your route accordingly.
- Scale – The scale of a terrain map represents the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. By understanding the scale of a terrain map, you can determine the actual distance between two points on the map.
- Grid – A grid is a series of intersecting lines that are drawn on a terrain map. The grid is used to locate specific features on the map and can be used to determine the distance between two points on the map.
- Legends – Legends are key to understanding the symbols used on a terrain map. Legends provide a guide to the symbols used on the map and explain what each symbol represents.
- Shading – Shading is used on terrain maps to represent changes in elevation. Lighter colors are used to represent higher elevations, while darker colors represent lower elevations. This shading provides a quick and easy way to visualize changes in elevation across the landscape.
- Compass Rose – The compass rose is a graphic that is used to show the orientation of the map. The compass rose indicates the direction of North, South, East, and West and is used to orient the map to the real world.
 Missouri Terrain Map
Missouri Terrain Map
Terrain maps are an incredibly valuable tool for a wide range of activities and professions. Whether you’re a hiker planning a route, a scientist studying the environment, or a geologist exploring the earth’s crust, terrain maps offer a range of benefits that can help you achieve your goals. Here are some benefits of terrain maps.
Navigation – One of the most obvious benefits of terrain maps is their use in navigation. Terrain maps provide a detailed and accurate representation of the landscape, including features such as rivers, mountains, and forests. By using a terrain map, you can navigate with confidence, knowing that you have a clear understanding of the terrain and the obstacles you may encounter.
Planning – Terrain maps are also incredibly useful for planning. Whether you’re planning a hiking trip, a geological survey, or an environmental study, terrain maps can help you identify the best route, locate important landmarks, and anticipate potential challenges.
Safety – Terrain maps can also play an important role in safety. By providing information about the landscape, including potential hazards such as cliffs, deep water, or steep slopes, terrain maps can help you avoid dangerous situations and stay safe while exploring the outdoors.
Environmental Study – Terrain maps are an essential tool for studying the environment. By providing detailed information about the topography of an area, terrain maps can help scientists and researchers understand the geology, hydrology, and ecology of a particular region.
Historical Study – Terrain maps can also provide valuable information about the history of an area. By studying historical terrain maps, researchers can gain insight into how the landscape has changed over time, including changes to land use, environmental conditions, and the impact of human activity.
Geology – Terrain maps are an essential tool for geologists. By providing information about the composition of the earth’s crust, including the location of rock formations and fault lines, terrain maps can help geologists understand the geological history of a particular region.
Recreation – Finally, terrain maps are an essential tool for outdoor recreation. Whether you’re hiking, camping, fishing, or simply exploring the outdoors, terrain maps can help you plan your activities, find the best routes, and discover new areas to explore.
Terrain maps are an incredibly valuable tool for a wide range of activities and professions. Whether you’re a hiker, a scientist, a geologist, or simply an outdoor enthusiast, terrain maps can provide you with the information you need to navigate, plan, and explore with confidence. So the next time you’re heading out into the great outdoors, be sure to bring along a terrain map and discover all the amazing benefits it has to offer.
Gallery of Terrain Maps with Google Maps Look
There are many sources available for terrain maps. WhiteClouds can help you with this process. Example terrain maps are shown below.
Gallery of Custom 3D Map Projects
Gallery of eCommerce 3D Raised Relief Maps
Shop WhiteClouds 3D Raised Relief Maps with 557,622 three-dimensional maps to choose from. These maps are not flat. They are three-dimensional, with the height being determined by Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data. These 3D maps are built by combining satellite imagery data from the USGS, Google Earth, Google Maps, and DEM data. Make a statement with these beautiful 3D map images from every part of the United States.
How 3D Terrain Maps are Made
There are several techniques used to create 3D terrain maps, and the process can vary depending on the scale and complexity of the map. However, the basic steps involved in making a terrain map are as follows:
- Create a base map. The first step in making a terrain map is to create a base map of the area. This can be done using imagery from a standard two-dimensional map, aerial photographs, satellite images, or WhiteClouds can do it for you.
- Determine the design style of the map. There are over 40 styles to choose from. Popular ones include satellite, terrain, topography, raised relief, and satellite hybrid.
- Add any special design features not included in the source map, such as special features, landmarks, legends, roads, cities, symbols, etc.
- Add elevation data. The next step is to add elevation data to the map. This can be done using a variety of techniques, such as contour lines, shading, or digital elevation models (DEMs).
- Print the Map Overlay. Latex vinyl materials are used for the map details and colors.
- Create the 3D physical map. Once the elevation data has been added to the map, a physical 3D structure is created that replicates the topography of the area. This can be done using 3D printed plastic or thermoformed molding/casting. Either approach is combined with the Vinyl overlay.
- Finish the map. This is where any excess materials are cutaway. Any special sealers, matte finishes, hardeners, or UV protection is applied. Wood, metal or plastic bases are built and border flocking may be applied.
Features & Benefits of Terrain Maps
- Remarkably Strong: You can drive a 1-ton truck over our terrain maps.
- Precision: We print our terrain maps to scale as accurately as are the original files and images.
- Excitement: It is much easier to get excited about 3D views of your topography than flat printed maps.
- Stain and Water Resistance: Spills are easy to wipe up.
- Communication: Terrain maps are simple to understand with a quick glance.
- Affordability: Our 3D technologies allow you to order custom 3D maps for a reasonable price.
- Testability: 3D technologies are affordable enough to test designs, such as several versions of planned work.
- Consistency: Using modern print and casting technologies, you can easily recreate identical 3D maps.
- Portability: We use lighter materials than what was available in the past, making our terrain and satellite maps easy to transport.
Videos of 3D Maps
Map Design Styles of Terrain Maps
Many design styles, or base maps, serve as a starting point for your terrain map. We source and create our base maps using the same digital tools that expert cartographers use to create maps. Once you have selected your base map, everything else is fully customizable. We can layer informational text (such as landmarks or other points of interest) and even change the colors to suit your preferences.
Complex layers can be added such as streams and lakes, terrain, roads, and even more detail like political boundaries, religious, and other population-based demographics. Multiple layers can also be added to the same terrain map. Take a look at the map style categories below for inspiration.
Technology and Materials Used in Terrain Maps
- With 3D printing technology, you are not limited to straight lines and boxes. The curves and cliffs are captured accurately and beautifully in astonishing detail.
- Your vision of the final 3D map determines which materials we will choose to produce the best results. We help you to determine the materials that best suit your project.
- We use fabrication technologies such as 3D printing, CNC cutting, and molding/casting.
- Terrain maps show incredible detail.
- Our maps are printed in full color (with over 17 million variations of color) for awe-inspiring presentations and displays. No painting required!
- Typically, we use a special process for finishing the sides of the raised relief maps in a suede-like material, similar to the finish of a jewelry box.
- Our in-house paint booth gives us flexibility in different types and grades of paint and finishing capabilities; we can provide UV-resistant coatings to protect the coloration of your 3M map for many years.
- We also offer customized additions to our 3D maps and models. Our in-house carpentry shop will build elegant bases, tables, or cabinetry to display any map you choose. Worried about dust? We can customize a case to protect your display as well. Our skilled artisans can hand-paint details to make your map a true work of art.
Pricing of Custom Terrain Maps
The price of 3D maps and models are generally based on your size requirements, specific design needs, and the amount of work it will take to produce. Each map is custom-built and charged for accordingly. The best way to determine cost is to email us, call us at 385-206-8700, or fill out the form below and let us bid on your project.
Get a Free Price Estimate for a Custom Terrain Map
Custom Fabrication Workflow
Common Questions & Answers
What is the largest map you can fabricate? There is no limit to the size of a map we can build. There are practical limits that will impact shipping and installation, but we work closely with our customers on these special requirements.
What type of 3D maps can you fabricate? All types. Satellite Maps, Terrain Maps, Topographical Maps, Raised Relief Maps, USGS Maps, Contour Maps, and many more.
Can you fabricate with different technologies and materials? Yes. Our most common fabrication technology is 3D Printing, but we can also build 3D Maps with CNC Cutting, 3D Foam, Molding/Casting, Thermoforming, and Sculpting.
What materials can you 3D print in? We match the correct material and fabrication process to your requirements in terms of presentation, size, and transportability. We can 3D print in PLA, FDM, Full-Color Sandstone, UV-cured resin, plastic, rubber-like, acrylic, and nylon – as well as combining multiple technologies.
Can you sign a Non-disclosure Agreement that you supply? Yes.
How long will it take to create my map? That depends on the design and size of the map. A more complex or detailed map will take longer than a simple map, we can’t really say exactly how long it will take until we have the chance to understand what type of map you want fabricated. Generally, smaller standard maps can be a couple of weeks and large museum exhibition maps can be 6 months.
What do you need from me to start the map fabrication? Boundaries are a good place to start. Determining map styles, sizes, height (may be exaggerated), and cabinetry needs are all part of the process. Special design features can also be added.
What are terrain maps? Terrain maps are graphical representations of the natural features of a particular geographic area, including its topography, vegetation, bodies of water, and other physical characteristics. These maps are commonly used by hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts to plan their routes and navigate through the landscape.
Terrain maps typically use a combination of contour lines, shading, and other symbols to convey information about the elevation, steepness, and other characteristics of the terrain. They may also include labels for prominent landmarks and features, such as mountain peaks and rivers.
What do terrain maps show? Terrain maps are visual representations of the natural features of a particular area, typically used to provide information about the terrain to those who are exploring or traveling through the area. These maps can show a variety of information, such as:
- Topography: The shape and elevation of the land, conveyed through the use of contour lines and shading.
- Bodies of water: Rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water, often labeled with their names and sometimes with additional information about their size and depth.
- Vegetation: Forests, fields, and other types of vegetation, which can be represented through the use of symbols or shading.
- Landmarks: Prominent features such as mountains, valleys, and cliffs, which are often labeled with their names and may be accompanied by additional information about their characteristics.
- Human-made features: Roads, buildings, and other man-made structures, which can be useful for navigation and planning travel routes.
How are terrain maps made? Terrain maps are made using a combination of modern technology and traditional cartographic techniques. Here are some of the key steps involved in creating a terrain map:
- Data collection: The first step in creating a terrain map is to collect data about the area being mapped. This can involve using satellite imagery, aerial photography, or other forms of remote sensing technology to capture detailed information about the landscape.
- Topographic surveying: To create accurate contour lines and elevation data, surveyors may also need to use more traditional techniques like ground-based surveying to capture precise measurements of the terrain.
- Data processing: Once the data has been collected, it is processed using specialized software to create a digital representation of the terrain. This may involve stitching together multiple images or data sets, removing any distortions or errors, and creating a 3D model of the landscape.
- Cartography: With the digital terrain model in hand, cartographers can begin the process of creating the map itself. This typically involves selecting appropriate symbols, colors, and other visual elements to convey information about the terrain.
- Finalization: Once the map is complete, it is reviewed and revised as needed to ensure that it accurately represents the terrain and provides the necessary information for users.
Who uses terrain maps? Terrain maps are used by a wide range of individuals and organizations, depending on their needs and interests. Here are some of the most common users of terrain maps:
- Hikers and outdoor enthusiasts: One of the primary users of terrain maps are hikers and other outdoor enthusiasts who need to navigate through unfamiliar terrain. These maps can help them plan their routes, avoid hazards, and identify points of interest along the way.
- Military personnel: Terrain maps are also used by military personnel for mission planning, navigation, and intelligence gathering. Military organizations may create their own specialized terrain maps with additional layers of information relevant to their operations.
- Scientists and researchers: Researchers in fields such as geology, ecology, and geography may use terrain maps to study the natural world, analyze landforms and natural processes, and plan fieldwork.
- Urban planners and developers: Terrain maps can also be useful for urban planners and developers who need to understand the natural features of a site and how they might impact development plans.
- Emergency responders: In the event of natural disasters or other emergencies, terrain maps can be invaluable for emergency responders who need to navigate through difficult terrain to reach people in need.
How do I read a terrain map? Reading a terrain map can seem daunting at first, but with a bit of practice and familiarity, it can become a valuable skill for anyone who enjoys exploring the outdoors. Here are some steps you can take to read a terrain map:
- Understand the legend: The legend or key is usually found in the corner of the map and explains the symbols and colors used on the map. This can include contour lines, symbols for vegetation and water features, and other information that is important to understanding the map.
- Identify the contour lines: Contour lines are the most important feature of a terrain map, representing the elevation and shape of the land. Contour lines that are close together indicate steep terrain, while widely spaced contour lines indicate flatter terrain.
- Look for other features: In addition to contour lines, terrain maps may include symbols for water features, vegetation, and human-made structures such as roads and buildings. These can provide additional information about the landscape and can be helpful in planning a route.
- Orient yourself: Terrain maps are usually oriented with north at the top, but it’s important to make sure you understand the direction and scale of the map before using it to navigate.
- Plan your route: Once you’ve familiarized yourself with the terrain map, you can begin planning your route. Look for areas with less steep terrain, avoid hazards such as cliffs and water features, and use landmarks and other symbols to guide your way.
How does a terrain map work? A terrain map works by representing the physical features of the landscape in a two-dimensional format. These maps use a variety of symbols, colors, and contour lines to convey information about the elevation, shape, and features of the terrain. Here’s how a terrain map works:
- Contour lines: One of the most important features of a terrain map is contour lines, which are used to represent the elevation and shape of the land. These lines connect points of equal elevation, allowing the viewer to visualize the three-dimensional landscape in a two-dimensional format.
- Colors and symbols: In addition to contour lines, terrain maps may use colors and symbols to represent different features of the landscape, such as vegetation, water features, and human-made structures like roads and buildings. These visual cues can help the viewer to better understand the terrain and plan their route.
- Scale: Terrain maps also include a scale that indicates the relationship between the distance on the map and the distance in the real world. This allows the viewer to estimate the time and effort required to travel through different parts of the landscape.
- Orientation: Most terrain maps are oriented with north at the top, allowing the viewer to orient themselves and navigate through the landscape.
What is the difference between a terrain map and a satellite map? A terrain map and a satellite map are two different types of maps that provide different types of information. Here’s how they differ:
- Information provided: A terrain map provides information about the physical features of the land, such as elevation, terrain, and vegetation. On the other hand, a satellite map provides information about the surface of the Earth, including man-made features like buildings, roads, and other infrastructure.
- Representation: A terrain map uses contour lines and symbols to represent the physical features of the land, while a satellite map uses actual photographs or images of the Earth’s surface.
- Scale: A terrain map typically covers a smaller area in more detail, while a satellite map can cover a larger area but may have less detail.
- Use: A terrain map is often used for navigation and exploring the natural world, while a satellite map is used for a variety of purposes, such as urban planning, monitoring land use changes, and analyzing environmental conditions.
What is a google terrain map? A Google Terrain Map is a type of online map provided by Google that displays the physical features of the Earth’s surface in detail. It is one of several types of maps available through Google Maps, which also includes satellite imagery, street maps, and hybrid maps.
A Google Terrain Map displays features such as elevation, terrain, and vegetation, and can be used to explore natural areas, plan hiking or biking routes, or study topography. The map includes contour lines, labels for prominent geographic features, and shading that indicates changes in elevation.
Users can zoom in or out to view the map at different levels of detail, and can toggle between different map types or overlay different layers, such as satellite imagery or street view. Google Terrain Maps are accessible through the Google Maps website or mobile app and can be used for a variety of purposes, including outdoor recreation, navigation, and education.
What features are on a terrain map? A terrain map displays a range of features that describe the physical characteristics of a landscape. Here are some of the key features that you might find on a terrain map:
- Contour lines: Contour lines are used to show the elevation and shape of the terrain. These lines connect points of equal elevation, allowing you to visualize the three-dimensional landscape in a two-dimensional format.
- Colors and shading: Colors and shading can be used to represent different types of vegetation, land cover, or other features of the terrain. For example, green might indicate forests or other dense vegetation, while brown might indicate bare ground or rock.
- Water features: Terrain maps often show bodies of water such as lakes, rivers, and streams. These may be labeled with their names and sometimes with information about their flow rate, depth, or other characteristics.
- Human-made features: Terrain maps may also show human-made features such as roads, buildings, and other infrastructure. These can be useful for navigation and for understanding the impact of human activity on the landscape.
- Landmarks and geographic features: Terrain maps may include labels or symbols for prominent geographic features such as mountain peaks, valleys, and canyons. These can help you identify and navigate through the landscape.
- Scale and orientation: Terrain maps also include a scale that indicates the relationship between distance on the map and distance in the real world. They are typically oriented with north at the top to allow the viewer to orient themselves and navigate through the landscape.
Do you have a question we didn’t answer? Don’t hesitate to contact us at 1-385-206-8700 or [email protected].
Worldwide Delivery
WhiteClouds has delivered maps around the world.
History of Terrain Maps
Terrain maps have a long and fascinating history that spans centuries of human exploration and discovery. From the earliest maps created by ancient civilizations to the highly detailed maps produced today, terrain maps have played an essential role in our understanding of the natural world.
The earliest terrain maps can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans. These maps were often highly stylized and symbolic, representing the landscape in a highly abstract and schematic form. While these early maps were limited in their accuracy and detail, they laid the foundation for the development of more advanced mapping techniques in the centuries that followed.
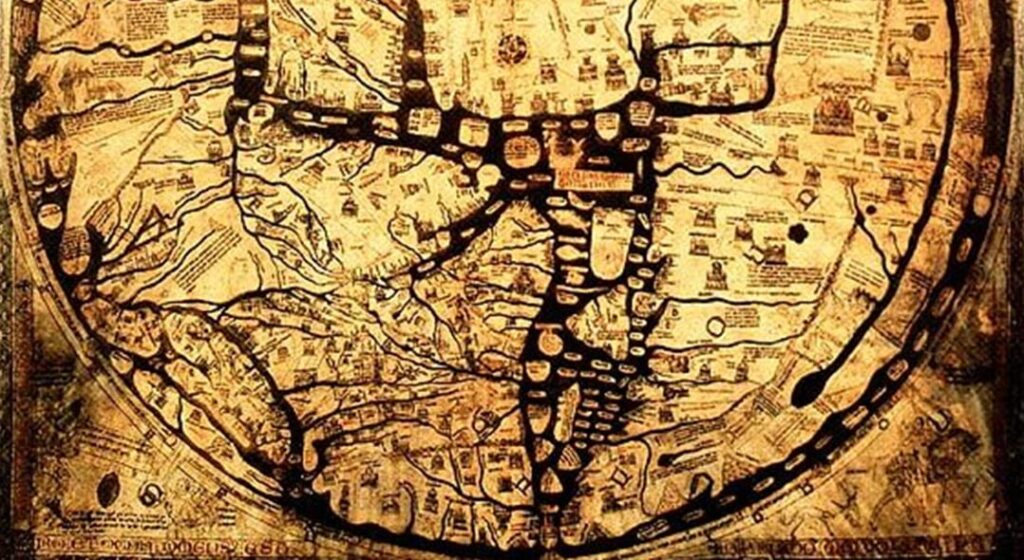
During the Middle Ages, maps began to evolve into more detailed and accurate representations of the landscape. These maps were often produced by monks and other scholars who were interested in studying the natural world. One of the most famous of these maps is the Mappa Mundi, a medieval map of the world that was created in the 13th century. This map included highly detailed illustrations of mountains, rivers, and other natural features, and served as a valuable tool for navigators and explorers.
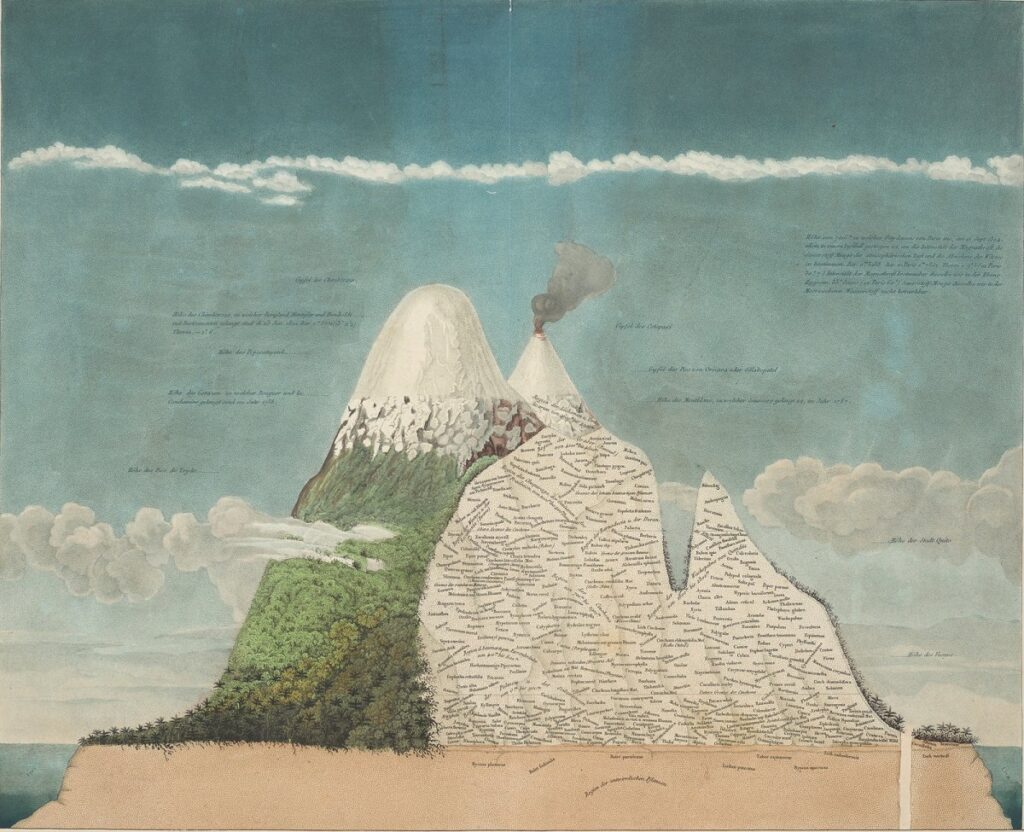
The 18th and 19th centuries saw significant advances in the field of cartography, as explorers and geographers began to map previously unexplored regions of the world. One of the most famous of these explorers was Alexander von Humboldt, a German naturalist and explorer who traveled extensively in South America and produced highly detailed maps of the region. These maps included detailed information about the geology, hydrology, and ecology of the region, and were instrumental in advancing our understanding of the natural world.
In the 20th century, terrain maps continued to evolve as new technologies and techniques were developed. One of the most significant advances was the development of aerial photography, which allowed cartographers to create highly detailed maps of the landscape from above. This technique was used extensively during World War II, as both Allied and Axis powers used aerial photography to create detailed maps of the terrain in Europe and Asia.
Today, terrain maps are produced using a variety of advanced technologies, including satellite imagery, LiDAR, and computer modeling. These techniques allow cartographers to create highly accurate and detailed maps of the landscape, including information about elevation, slope, and other important features.
The history of terrain maps is a rich and fascinating story that spans centuries of human exploration and discovery. As we continue to explore and study the earth’s surface, it’s clear that terrain maps will continue to play an important role in our ongoing efforts to map and understand the world around us.