Luki Crater
Luki Crater
We Build Custom 8K Mars Canvas Prints of Luki Crater
Luki Crater
Luki Crater, though not as widely recognized as some of its Martian counterparts, holds a unique place of scientific importance when it comes to understanding the geological history of the Red Planet. Characterized by a rich tapestry of features, ranging from sedimentary deposits to possible signs of ancient fluvial activity, Luki Crater serves as a captivating subject for researchers aiming to decode the enigmas of Mars’ multifaceted past. Named after a quaint village in Russia, the crater has increasingly become the focal point of an array of scientific investigations. These studies not only aim to unravel the complexities of Martian history but also seek to shed light on broader questions surrounding planetary formation and evolution.
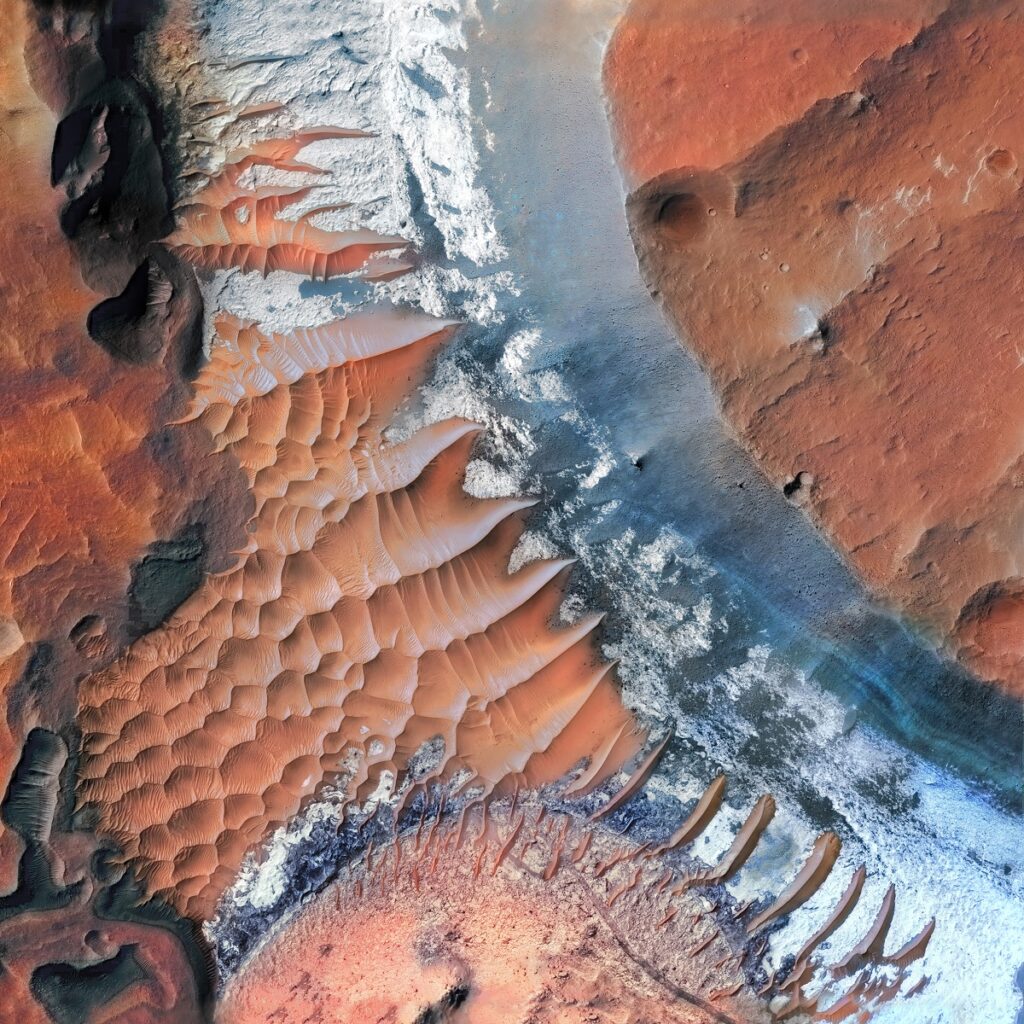
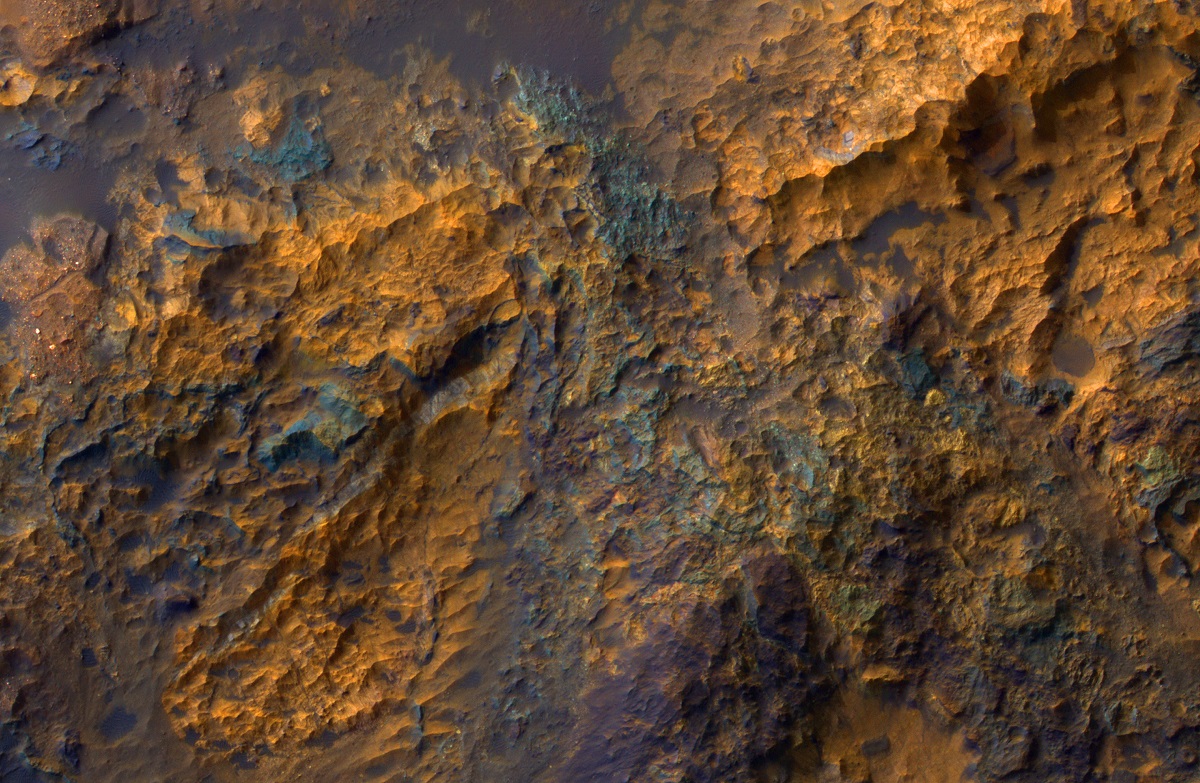 Luki Crater in the Southern highlands
Luki Crater in the Southern highlands
Geographical Location
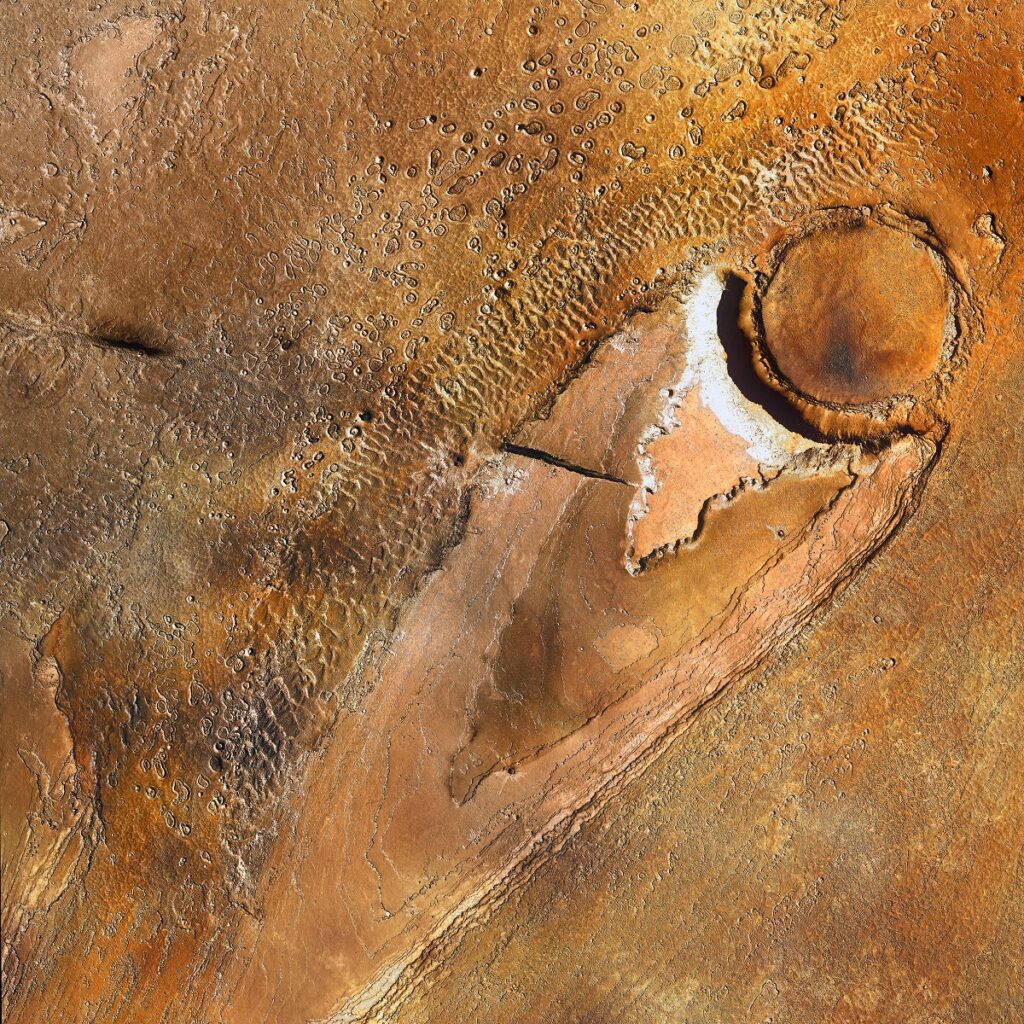
Luki Crater finds its home in the Southern Hemisphere of Mars, nestled within the Hellas quadrangle. This quadrangle is particularly famous for the Hellas Planitia, one of the largest known impact basins in the solar system. The crater itself is specifically situated at coordinates around 45.5°S latitude and 268.4°E longitude. Unlike some craters on Mars, Luki Crater isn’t lost in a sea of similar features but stands out in a Martian landscape rich with a plethora of geological formations. These include ancient river valleys, expansive lava plains, and sedimentary rock layers. Spanning a diameter of approximately 20 kilometers, Luki Crater occupies a unique position in the echelon of Martian craters; it’s not too large to be classified among the giant craters nor too small to be overlooked. This moderate size, combined with its geographical context—especially its proximity to the awe-inspiring Hellas Planitia—makes Luki Crater a prime subject for multifaceted scientific investigation, including the study of impact dynamics and geological processes.
Geological Composition
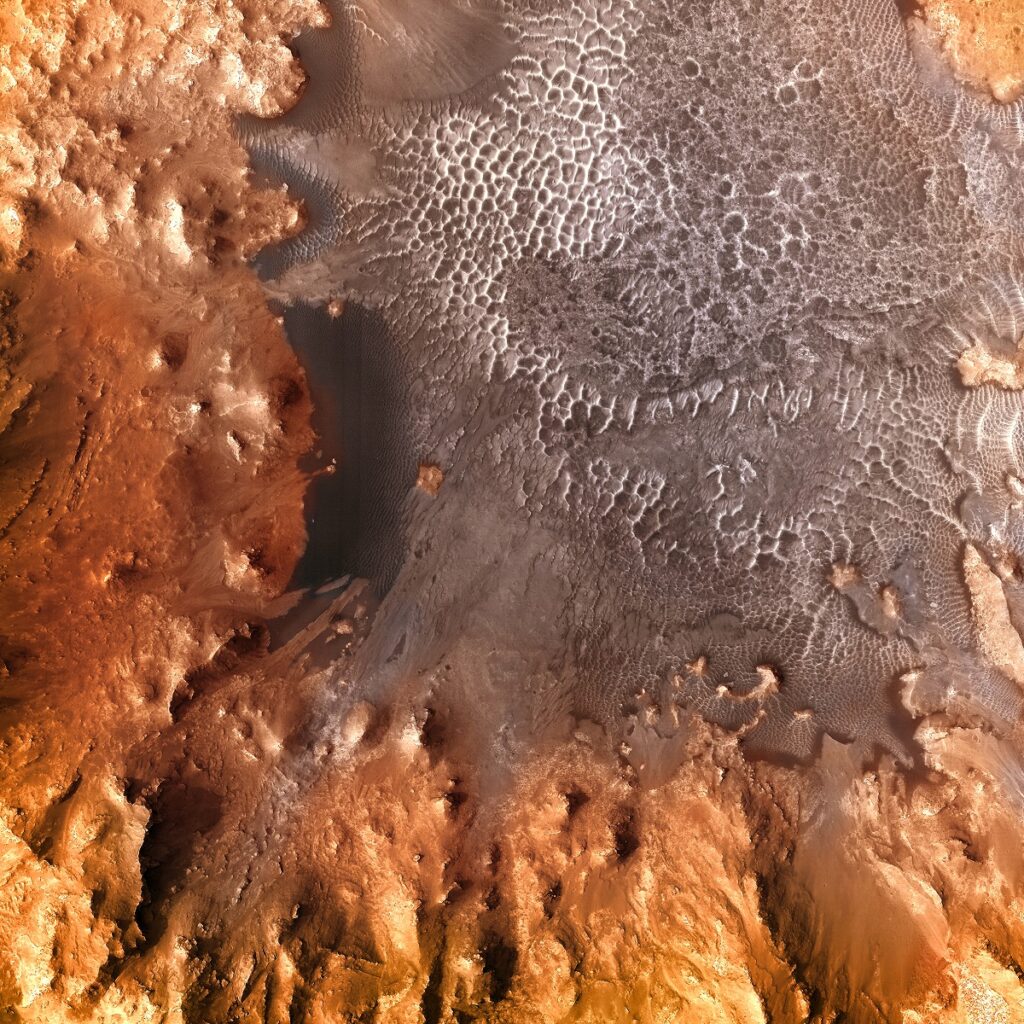
Luki Crater offers a rich and intricate geological tapestry that has fascinated scientists. The bedrock of the crater consists predominantly of sedimentary layers. These layers show evidence of having undergone various processes such as aeolian (wind-driven) and fluvial (water-driven) erosion and sedimentation. Spectroscopic data have unearthed an elaborate mineralogical palette, featuring a blend of sulfates, clays, and intriguingly, remnants of what could be ancient evaporite deposits. These evaporites are particularly exciting as they suggest that this region may have once been the bed of a standing body of water like a lake. Alongside these sedimentary features, Luki Crater also displays signs of volcanic activity, evident from its basaltic compositions in specific sections. Further complicating its geological history are signs of impact melt and breccias—rock fragments fused together during the high-energy impact event that created the crater. These elements add intricate layers of complexity, making Luki Crater a captivating subject for studying planetary geology.
Significant Discoveries
Ancient Fluvial Systems
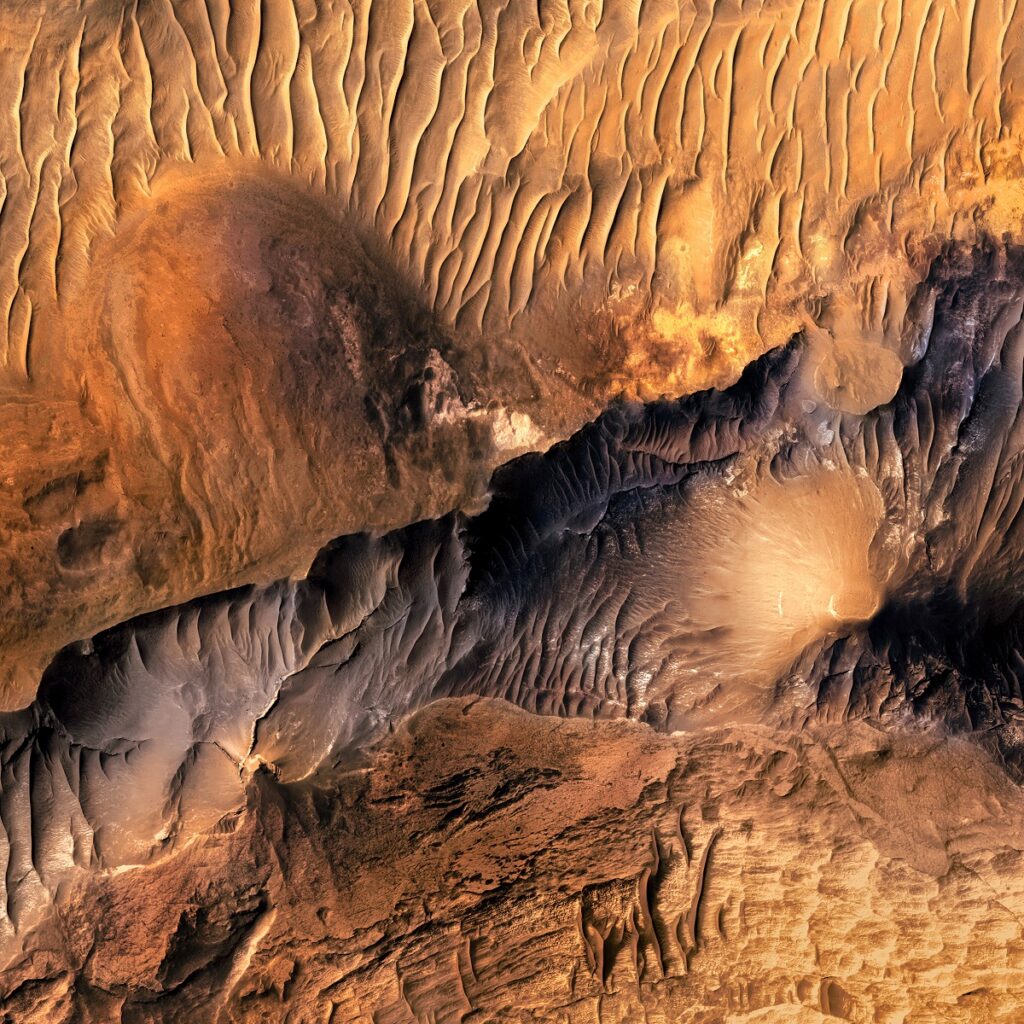
Among the headline discoveries at Luki Crater are compelling signs of ancient fluvial systems. The crater floor and walls feature distinct geomorphological markers, including gullies, valleys, and what look like fossilized riverbeds. These features strongly indicate that water once flowed here, carving out the landscape and contributing to the formation of the sedimentary layers that we observe today.
Mineralogical Evidence of Water
Another revolutionary discovery was the identification of sulfate and clay minerals through spectroscopic analyses. These mineral types typically form in aqueous environments, bolstering the hypothesis that Luki Crater was once home to a body of water—perhaps a lake or a series of interconnected ponds.
Impact History
The crater has also revealed significant clues about its own history and, by extension, the history of Martian impacts. The presence of impact melts and breccias have provided researchers with critical tools for radiometric dating and have supplied valuable data on the rate of cratering on Mars, contributing to broader theories of planetary evolution.
Scientific Missions
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has been instrumental in our understanding of Luki Crater. Employing its high-resolution cameras and spectrometers, the MRO has generated an impressive collection of imagery and data that have been vital for the identification and study of both geological and geomorphological features of the crater.
Mars Odyssey
The Mars Odyssey spacecraft has also significantly contributed to our knowledge of Luki Crater. Its Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) instrument has been especially useful, generating thermal and mineralogical maps that have shed light on the crater’s complex geological composition. These maps have also offered tantalizing clues about potential ancient hydrothermal systems in the region.
Geomorphological Features
The geomorphological features of Luki Crater are as detailed and intricate as its geological composition. Prominent among these are central peaks and terraced walls, typical features in complex impact craters. A rich network of gullies, valleys, and other erosional features crisscrosses the crater’s surface, which is believed to have been shaped largely by ancient fluvial processes. Exposed sedimentary layers along the crater’s walls act like a geological textbook, each layer representing a chapter that helps researchers understand the chronological sequence of Martian geological and environmental events. This complex tapestry of features not only makes Luki Crater an object of scientific curiosity but also a window into the history of Martian geological and climatic changes.
Luki Crater stands as a fascinating subject in Martian geological studies, offering a blend of complex features and intriguing discoveries. Its geological composition and geomorphological features tell a compelling story of ancient water systems, volcanic activity, and impact processes. Scientific missions to Mars continue to reveal more about this unique crater, making it a subject of ongoing interest in our quest to understand the Red Planet’s history and, perhaps, its potential for past habitability.
Check out our 3D Mars Learning Center for more information on Mars and Luki Crater. You can also learn more at: NASA Mars Exploration.
More About Mars
Contact us today to learn more about our 3D services and how we can help you achieve your goals.





