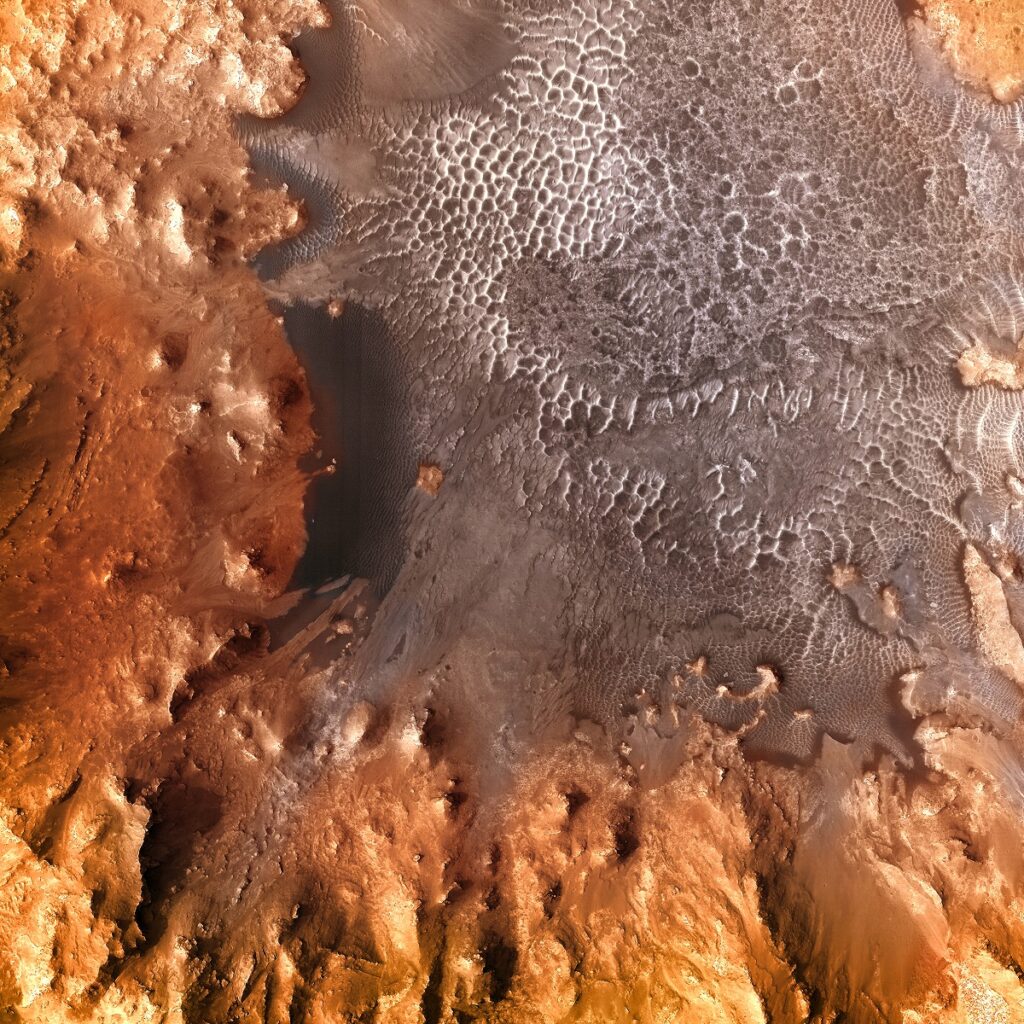
Holden Crater
Holden Crater
We Build Custom 8K Mars Canvas Prints of Holden Crater
Did you know we make
custom
8K Mars Canvas Prints

and
3D Marscapes

Holden Crater
Holden Crater is one of the most captivating geological features on Mars, often cited for its potential in revealing secrets about the Red Planet’s history, particularly its past climate and the presence of water. As a focal point for numerous scientific missions, the crater has been extensively studied to understand its complex geomorphology, mineralogy, and the possible implications these have for astrobiology.
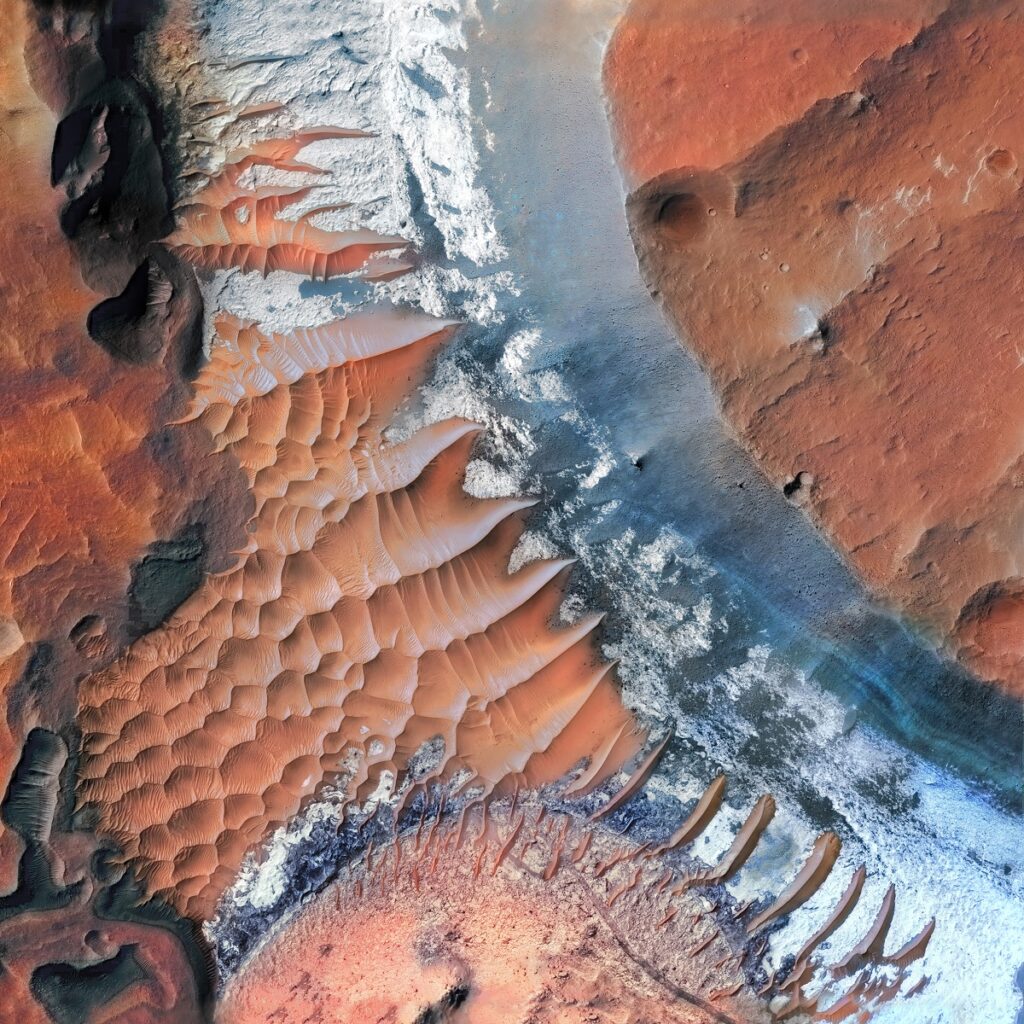
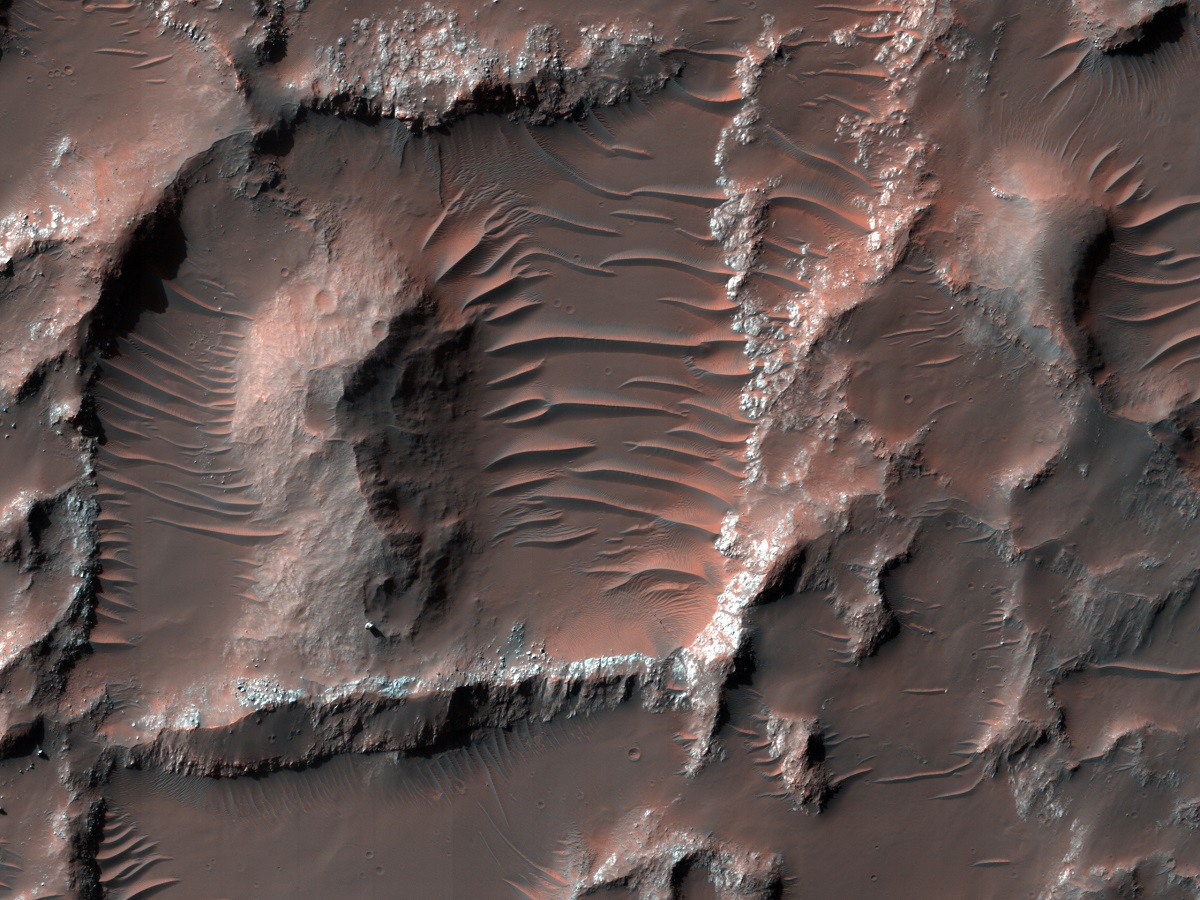 Complex Terrain East of Holden Crater
Complex Terrain East of Holden Crater
Geographical Location
Holden Crater occupies a critical position in the Martian landscape, situated at approximately 26.4°S latitude and 325.4°E longitude in the southern highlands of Mars. This crater, with its expansive diameter covering an estimated 154 kilometers, lies to the southeast of the massive Eberswalde Crater. What sets Holden Crater apart is its location within one of the oldest terrains on the Martian surface, potentially serving as a geological vault containing records spanning millions of years. Further augmenting its significance is its close proximity to ancient river valleys and outflow channels, which are themselves areas of intense scientific scrutiny. These adjacent features could hold answers to long-standing questions about Mars’ aqueous history and geomorphological evolution. Holden Crater’s optimal location, enveloped by such a rich array of geological attributes from diverse epochs, places it squarely in the crosshairs of scientific inquiry and exploration.
Advertisement
Sample Marscapes
Geological Composition
The geological narrative within Holden Crater is an intricate blend of multiple eras from Mars’ deep geological history. Initially formed by a cataclysmic impact event, the crater has been subjected to an array of subsequent geological phenomena, including volcanic activity, sediment deposition, and erosional processes. Advanced spectroscopic studies have unveiled a fascinating spectrum of minerals within the crater, most notably clays and sulfates, both of which are water-associated minerals. The presence of these minerals lends credence to the hypothesis that Holden Crater was possibly part of an extensive lake system or even an ancient river delta at some point in its history. The well-defined stratified layers in the crater’s walls function like a geological almanac, capturing various episodes of sediment deposition and erosional events. These strata are invaluable for interpreting different environmental and possibly climatic conditions over vast stretches of Martian history.
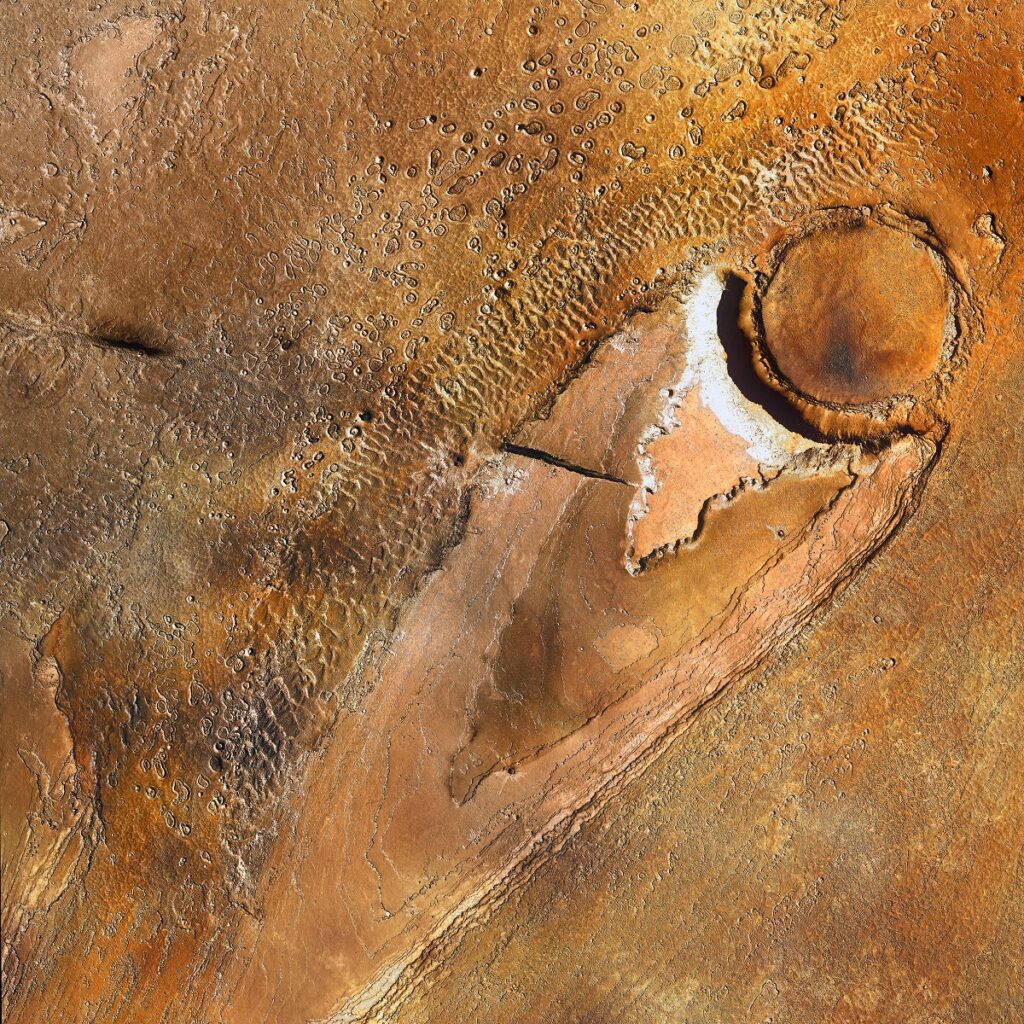
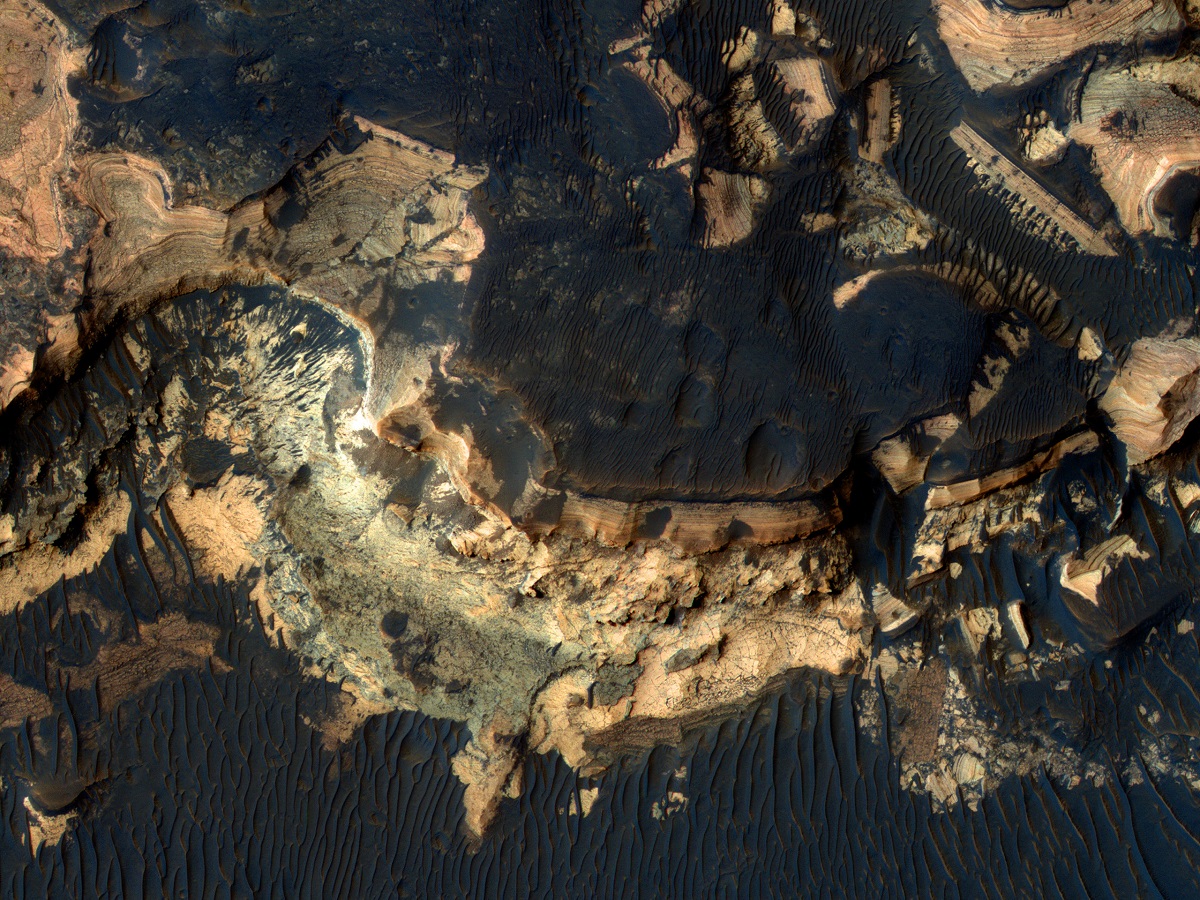 Candidate Landing Site in Holden Crater
Candidate Landing Site in Holden Crater
Significant Discoveries
Past Aqueous Activity
Holden Crater has offered compelling evidence for a history teeming with water-based activities. Spectroscopic data and high-resolution imagery have revealed formations of sedimentary rocks, intricate fluvial fan structures, and a spectrum of water-related minerals. These elements together create a compelling argument that the area might have harbored bodies of water, possibly lakes, or even formed part of a more complex water system at one point in time.
Stratigraphic Records
The visible layers of rock and sediment on the crater’s walls are akin to the pages of a book, recording the planet’s geological and possibly climatic chronicles. These stratified layers represent diverse episodes in Martian history, from periods of sedimentation to erosion, thereby serving as a repository of knowledge that could elucidate the geological timeline and changing environmental conditions of the planet.
Astrobiological Potential
The synthesis of aqueous history and the diverse mineralogical composition of Holden Crater sparks intriguing questions about the astrobiological potential of the area. Could the water bodies that likely existed here have been habitable environments for microbial life? Moreover, if life ever existed, could its signatures be fossilized within the sedimentary layers or mineral deposits that we see today?
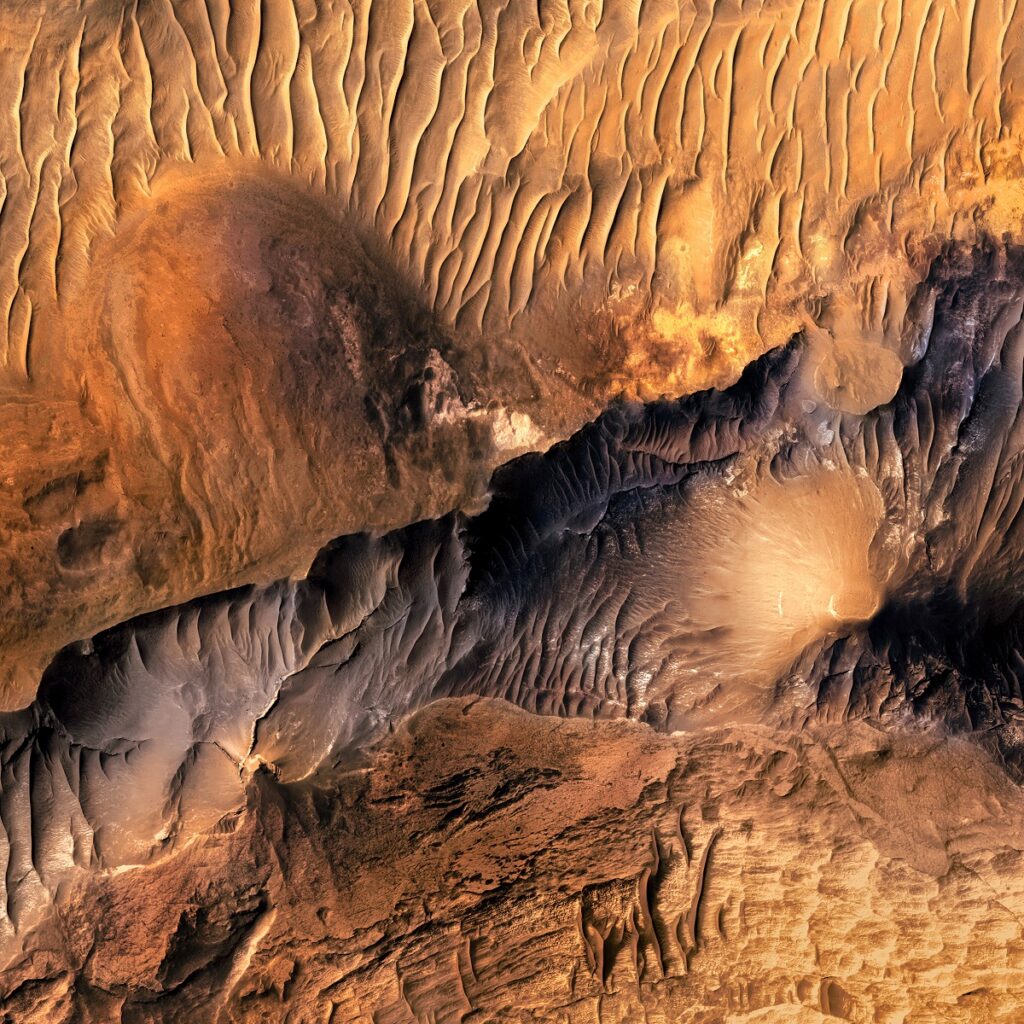
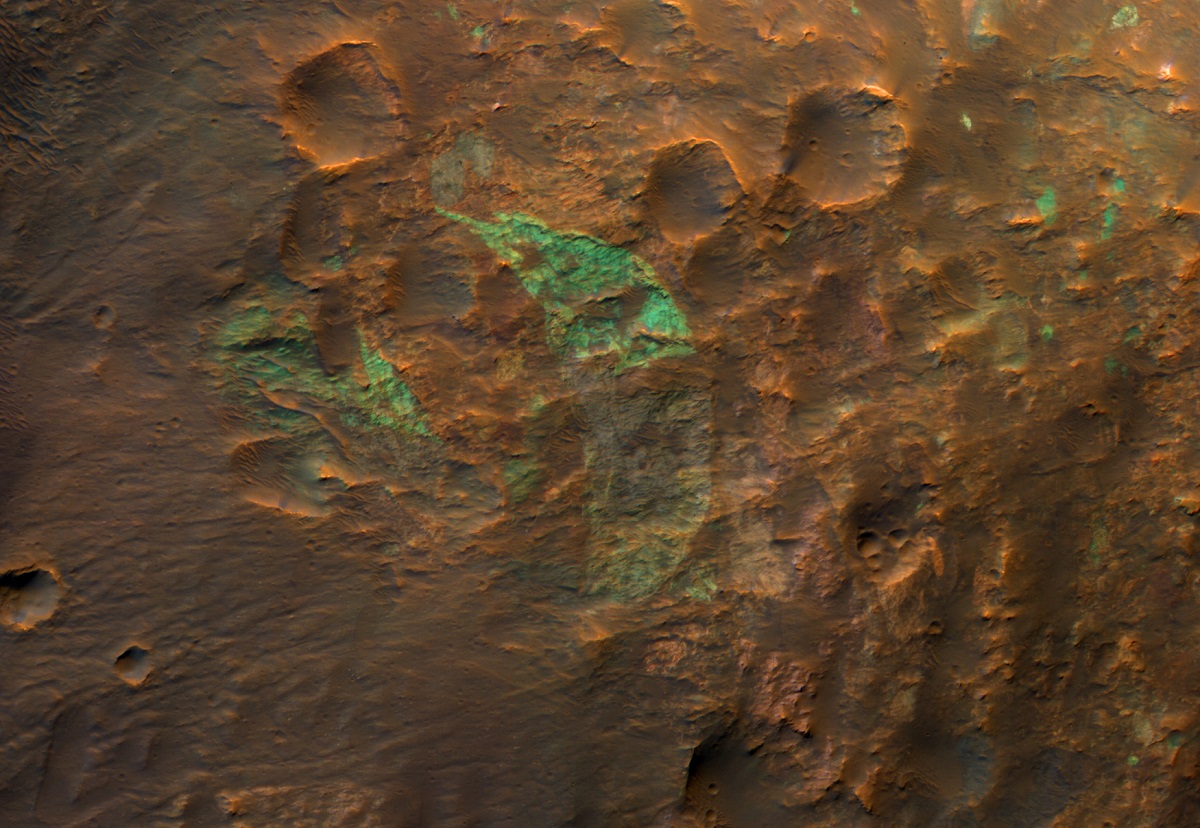 Cubism in the Western Rim of Holden Crater
Cubism in the Western Rim of Holden Crater
Scientific Missions
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO)
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has been instrumental in our current understanding of Holden Crater. Its high-resolution cameras and spectroscopic instruments have delivered detailed analyses of the crater’s geological and mineralogical characteristics, providing the kind of data that serves as a foundation for all subsequent studies.
Curiosity Rover
Although the Curiosity Rover hasn’t directly explored Holden Crater, it has conducted missions in regions not far from it. The data gleaned from Curiosity’s explorations offer complementary context that contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of Holden Crater’s geological features and historical significance.
Geomorphological Features
Holden Crater is adorned with an eclectic collection of geomorphological features that add to its complexity. Among them are expansive alluvial fans, layers upon layers of sedimentary deposits, and finely etched erosional patterns that are a confirmation to various geological processes acting over time. The crater floor is particularly interesting, showcasing what look like remnants of ancient river channels. This elaborate network of features indicates a history shaped by a myriad of forces: from the initial impact that formed the crater, to periods of water flow, to the action of Martian winds eroding its surface. Each of these elements contributes to the intricate geological tapestry that is Holden Crater.
Holden Crater serves as a remarkable natural laboratory for understanding Mars’ complex geological and environmental history. Its prime location, diverse geological composition, and the plethora of significant discoveries it has yielded make it an invaluable resource for future scientific exploration and study. The questions it raises about Mars’ past climate, potential for life, and geological evolution make it not just a crater on a distant planet, but a key to understanding the broader universe.
Check out our 3D Mars Learning Center for more information on Mars and Holden Crater. You can also learn more at: NASA Mars Exploration.
More About Mars
Contact us today to learn more about our 3D services and how we can help you achieve your goals.









